Introduction
Intimate depigmentation, a phenomenon that has gained attention in recent years, refers to the lightening or discoloration of the skin in intimate areas such as the genitalia, anal region, and underarms. While the topic may seem taboo, it is crucial to shed light on the reasons behind intimate depigmentation in women and explore potential remedies. In this comprehensive blog post, we will delve into the causes of intimate depigmentation and discuss various remedies to address this concern.
Causes of Intimate Depigmentation
1. Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal fluctuations play a significant role in intimate depigmentation. Changes in estrogen levels, especially during pregnancy or menopause, can affect melanin production in the skin. This hormonal imbalance may lead to pigmentation changes in intimate areas.
2. Friction and Irritation:
Continuous friction and irritation in intimate areas, often caused by tight clothing or excessive rubbing, can contribute to depigmentation. The constant rubbing can damage the delicate skin in these regions, leading to inflammation and changes in pigmentation.
3. Ageing:
As women age, the skin undergoes natural changes, including a reduction in collagen and elastin production. This can result in thinner and more delicate skin, making it susceptible to pigmentation changes. The intimate areas may show signs of depigmentation as a part of the ageing process.
4. Genetics:
Genetic factors can also play a role in intimate depigmentation. Some individuals may be more predisposed to pigmentation changes due to their genetic makeup. Understanding one's family history can provide insights into the likelihood of experiencing depigmentation.
5. Inflammatory Conditions:
Skin conditions such as lichen sclerosus or vitiligo, which involve inflammation or the destruction of pigment-producing cells, can contribute to intimate depigmentation. These conditions may affect the skin's ability to maintain its natural color in intimate areas.
6. Chemical Irritants:
The use of harsh chemical products in intimate areas, such as certain douches, soaps, or depilatory creams, can lead to skin irritation and depigmentation. Chemicals in these products may disrupt the skin's natural balance, causing pigmentation changes over time.
Remedies for Intimate Depigmentation
1. Topical Treatments:
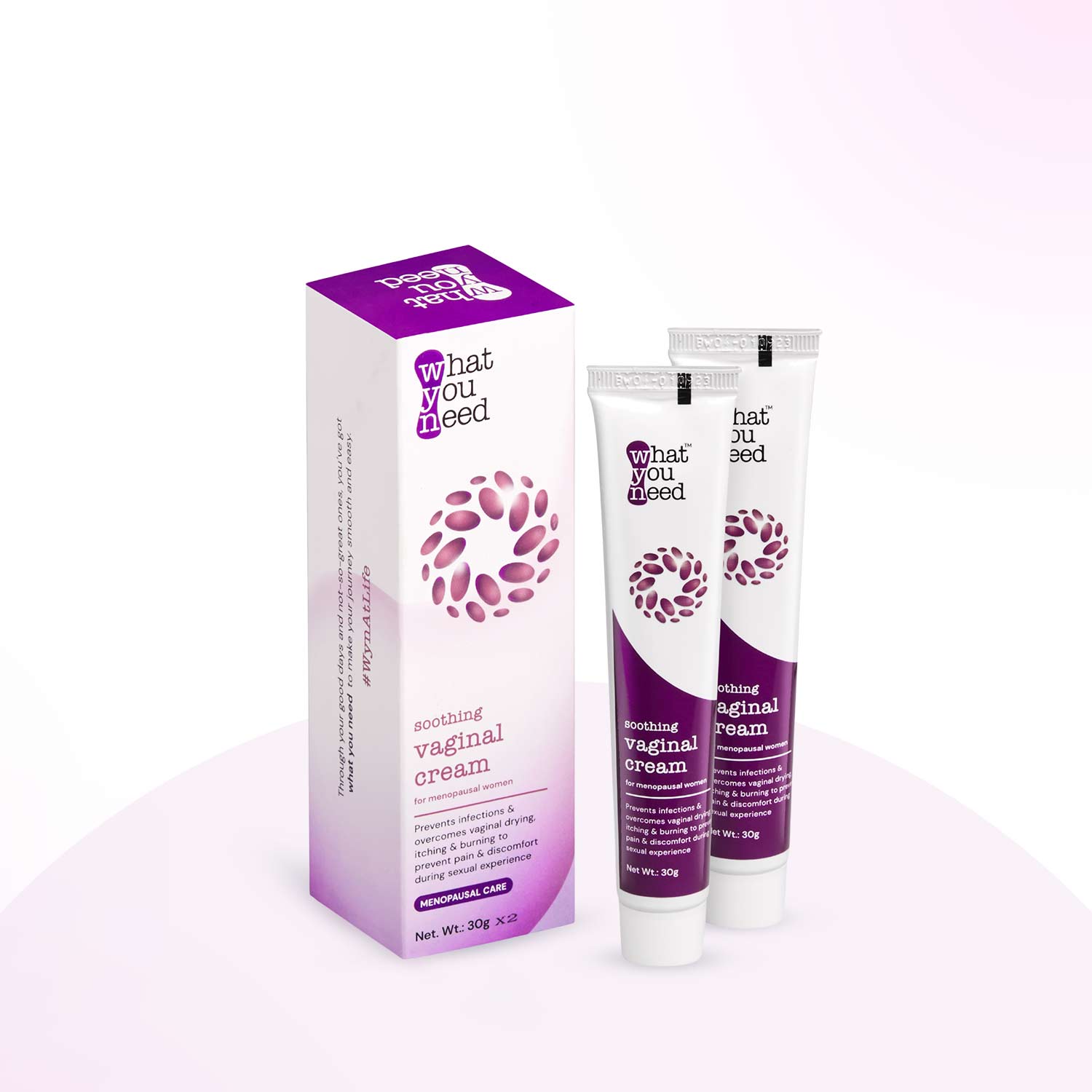
There are various topical treatments available that may help address intimate depigmentation. Ingredients such as niacinamide, alpha arbutin, and licorice extract have been reported to have skin-lightening properties. However, it is essential to consult with a dermatologist before using any products in sensitive areas to ensure safety and effectiveness.
2. Laser Therapy:
Laser therapy, specifically targeted at pigmented areas, can be an effective solution for intimate depigmentation. This non-invasive procedure works by breaking down excess melanin, leading to a more even skin tone. Consultation with a dermatologist is crucial to determine the suitability of this treatment for individual cases.
3. Hormonal Management:
For cases related to hormonal changes, hormonal management may be considered. This could involve hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for menopausal women or other hormonal interventions to balance estrogen levels. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to explore suitable options.
4. Avoidance of Irritants:
Preventing further irritation in intimate areas is crucial. This involves choosing breathable and comfortable clothing, avoiding harsh soaps and chemicals, and practicing good hygiene. By minimizing friction and irritation, the risk of depigmentation can be reduced.
5. Healthy Lifestyle Choices:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can positively impact skin health. Adequate hydration, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, and regular exercise contribute to overall well-being and may support skin health, including in intimate areas.
6. Consultation with Healthcare Professionals:
It is crucial to consult with dermatologists or gynecologists for personalized advice and treatment plans. Professionals can assess individual cases, identify underlying causes, and recommend appropriate interventions tailored to the specific needs of the individual.
Conclusion
Intimate depigmentation in women is a multifaceted issue influenced by various factors, ranging from hormonal changes to genetic predispositions. While addressing depigmentation is a personal choice, understanding the causes and exploring remedies can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their skin health. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals ensures a holistic approach to managing intimate depigmentation, promoting both physical and emotional well-being. By fostering open conversations about this topic, we can contribute to destigmatizing intimate skin concerns and promoting a more inclusive understanding of women's health and women’s wellness.
FAQs
What causes intimate hyperpigmentation in women?
Intimate hyperpigmentation in women, also known as darkening of the skin in the genital and anal areas, can result from various factors. Hormonal changes play a significant role, particularly during pregnancy and childbirth, where increased melanin production can lead to discoloration. Hormonal fluctuations related to contraceptives or menopause may also contribute.
Friction and irritation from tight clothing, frequent shaving, or aggressive hair removal methods can cause inflammation, prompting the skin to produce more melanin as a defense mechanism. This is common in areas prone to chafing and rubbing.
Infections, such as fungal or bacterial, can lead to hyperpigmentation as the body responds to inflammation. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) may also contribute, emphasizing the importance of safe sexual practices.
Skin conditions like lichen sclerosus or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation can affect intimate areas. Additionally, exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation without proper protection can exacerbate pigmentation changes.
While these factors may contribute to intimate hyperpigmentation, it's essential for individuals experiencing such changes to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management, as treatments may vary based on the underlying cause.
Why does intimate area get dark in women?
Intimate areas in women can darken due to a variety of factors, and understanding these causes is crucial for proper care and management. Hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy, childbirth, or menopause, can stimulate increased melanin production, leading to hyperpigmentation. This natural response to hormonal fluctuations is a common cause of darkening in intimate areas.
Friction and constant irritation, often stemming from tight clothing, aggressive shaving, or harsh hair removal methods, can result in inflammation. In response, the skin produces more melanin, contributing to the darkening of these sensitive regions.
Infections, both fungal and bacterial, may cause inflammation and pigmentation changes in intimate areas. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can also be a factor, emphasizing the importance of practicing safe sex.
Certain skin conditions, such as lichen sclerosus or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, may affect the intimate areas and contribute to darkening. Additionally, prolonged exposure to UV radiation without proper protection can intensify pigmentation changes.
Women experiencing darkening in intimate areas should seek professional medical advice for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment. Consulting with a healthcare provider ensures a comprehensive understanding of the underlying causes and appropriate steps for addressing intimate hyperpigmentation.
What is intimate depigmentation of women?
Intimate depigmentation in women refers to the process of lightening or reducing pigmentation in sensitive areas such as the genital, anal, and surrounding areas. This cosmetic procedure is sought for various reasons, including aesthetic preferences, cultural considerations, or addressing hyperpigmentation concerns in intimate regions.
The depigmentation process often involves the use of topical agents or treatments that aim to inhibit melanin production, the pigment responsible for skin color. Ingredients like hydroquinone, kojic acid, and alpha-arbutin are commonly used to lighten the skin by suppressing melanin synthesis.
Women may opt for intimate depigmentation to achieve a more uniform skin tone, address dark spots or hyperpigmentation caused by hormonal changes, inflammation, or other factors. It is important to note that this procedure should be performed by trained professionals in a clinical setting to ensure safety and minimize potential side effects.
While intimate depigmentation is a personal choice, individuals considering this cosmetic procedure should carefully weigh the risks and benefits, consult with a qualified dermatologist or healthcare professional, and ensure that the treatment aligns with their individual goals and well-being.
How do you treat intimate pigmentation of women?
Treating intimate pigmentation in women involves a multifaceted approach, and the specific method depends on the underlying cause. It's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist for a personalized treatment plan.
1. Topical Agents: Dermatologists often prescribe topical treatments containing ingredients like hydroquinone, kojic acid, arbutin, or vitamin C. These agents work by inhibiting melanin production, gradually lightening the pigmented areas.
2. Chemical Peels: Mild chemical peels containing alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) can help exfoliate the skin, reducing hyperpigmentation. This procedure is typically performed by skincare professionals.
3. Laser Therapy: Various laser treatments, such as intense pulsed light (IPL) or fractional laser therapy, can target pigmented areas and stimulate collagen production. Laser treatments should be administered by trained professionals.
4. Microdermabrasion: This non-invasive procedure involves removing the outer layer of skin, promoting new skin cell growth and potentially reducing pigmentation.
5. Hormonal Management: If hormonal changes contribute to pigmentation, hormonal therapies or contraceptives may be considered under medical supervision.
Regardless of the chosen method, it's essential to prioritize sun protection, as UV exposure can exacerbate pigmentation issues. Additionally, practitioners should conduct a thorough assessment to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on individual needs and skin types.
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Opens in a new window.